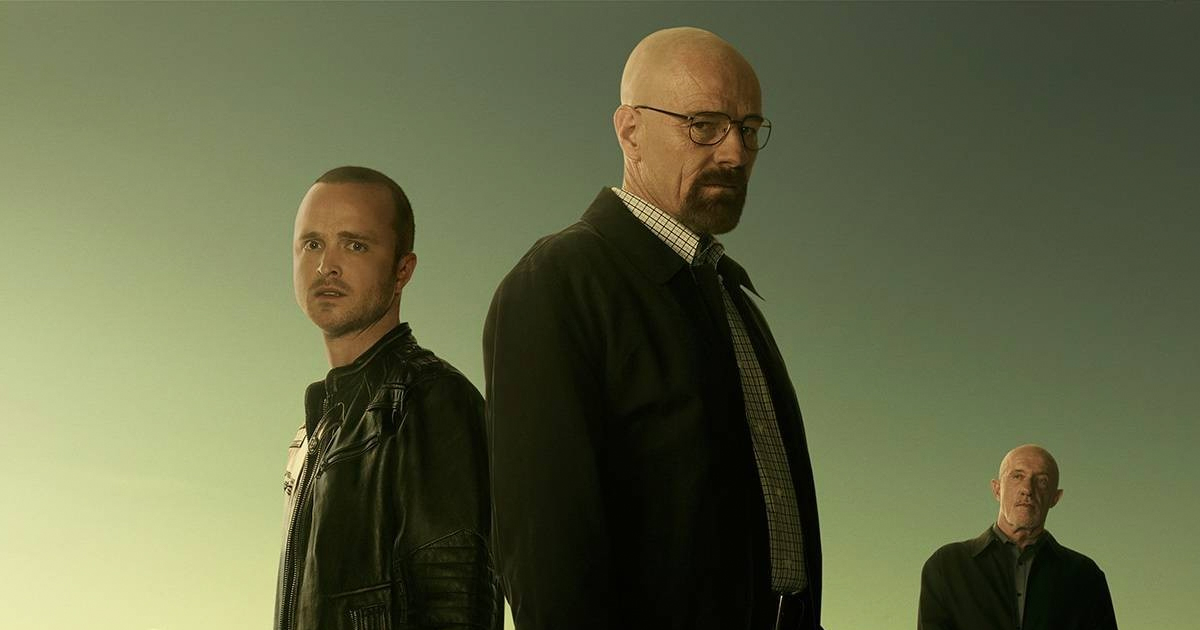
Television ratings are an essential tool for gauging the popularity and viewership of TV shows. They provide valuable data for producers, networks, and marketers to plan advertising and programming strategies. They also help viewers understand the likelihood of their favorite shows being renewed or not. So how do television ratings work, and how are accurate viewer numbers measured?
What are TV ratings?
TV ratings are numbers that show how many individuals are watching a particular program at a certain time. Companies like Nielsen are responsible for collecting this data through methods like surveys, electronic devices, and metering systems.
Rating agencies commonly use Nielsen meters in specific households to track channel viewing habits, which are then used to estimate viewership patterns across the entire population.
How data is collected
Information is gathered primarily from smart TVs, electronic set-top boxes, and metering systems. These devices send viewing data directly to the agency, offering a more comprehensive view of audience behavior. A major benefit of this technology is that it provides real-time data collection and eliminates the need for manual input.
There's more to television ratings than merely counting the number of people watching—they also offer demographic breakdowns based on age, gender, income, and ethnicity. Advertisers can benefit greatly from this demographic data so that they can target content to audiences that would be most likely to be positively receptive to their content. Viewer surveys are also conducted to gather more demographic data.
Limitations of data collection
TV ratings have limitations even though they provide insightful information. The rise of alternate watching platforms—like streaming services and mobile devices—that aren't always taken into account by conventional rating systems presents one difficulty. Commercial ratings—a measure of how viewers interact with advertisements—also provide a challenge for networks and marketers.
For data to be significant, it must also be collected from a sufficient sample size. Ensuring that the sample size is representative is a key factor in television ratings. Rating agencies select families for their measurement panels to accurately reflect the diversity of viewers. Statistical modeling techniques are then used to project the sample data to the entire population.